distribution of a box plot positive and negative skew Positive skew means a tail stretching right, while negative skew veers in the opposite direction. Kurtosis is all about peaks and tails. High kurtosis sharpens peaks and weighs down the tails, while low kurtosis spreads data, . The plan for this project is to remove the old sink and countertop, prep the cabinet, install the new sink, set the new counters, then install the faucet and connect the plumbing. If your new top is stone, a countertop installer is going to measure the cabinets and sink to .
0 · skewed right box plot
1 · right skewed box plot vertical
2 · positively skewed box and whisker
3 · positive skewness boxplot
4 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
5 · plot skewed to the right
6 · boxplot left skewed or right
7 · box and whisker plot skewness
Our craftsmen design, lay out, measure, fabricate, and install sheet metal products to meet your need for just about anything to be made out of metal. We are approved by all major roofing material manufacturers to install, maintain, repair, and replace their products.
In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to . When working with skewed distributions, it is essential to understand the key differences and similarities between positive and negative skewness. Both types of skewness exhibit asymmetrical shapes, but they .
Positive skew means a tail stretching right, while negative skew veers in the opposite direction. Kurtosis is all about peaks and tails. High kurtosis sharpens peaks and weighs down the tails, while low kurtosis spreads data, .
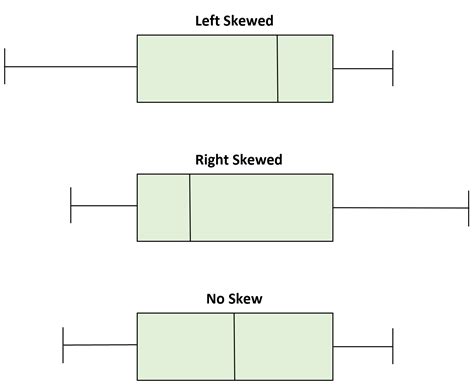
A negative value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the left side of the distribution, which extends towards more negative values. A positive value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the right side of the distribution, . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum . Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of a distribution. A distribution is asymmetrical when its left and right side are not mirror images. A distribution can have right (or positive), left (or negative), or zero skewness.
A distribution is considered "Positively Skewed" when mean > median. It means the data constitute higher frequency of high valued scores. Negatively Skewed : For a distribution that is negatively skewed, the box plot will show the median .
Skewness of Box Plots. A box plot has positive skew if the median is nearer to the start of the plot and the first whisker is shorter than the last whisker. There is negative skew if the median is nearer to the end of the plot and the last .
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, . We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics of the symmetrical normal distribution with skewed distributions. When working with skewed distributions, it is essential to understand the key differences and similarities between positive and negative skewness. Both types of skewness exhibit asymmetrical shapes, but they differ in the direction of the skew. Positive skew means a tail stretching right, while negative skew veers in the opposite direction. Kurtosis is all about peaks and tails. High kurtosis sharpens peaks and weighs down the tails, while low kurtosis spreads data, lightening the tails. A negative value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the left side of the distribution, which extends towards more negative values. A positive value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the right side of the distribution, which extends towards more positive values.
skewed right box plot
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
right skewed box plot vertical
Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of a distribution. A distribution is asymmetrical when its left and right side are not mirror images. A distribution can have right (or positive), left (or negative), or zero skewness.A distribution is considered "Positively Skewed" when mean > median. It means the data constitute higher frequency of high valued scores. Negatively Skewed : For a distribution that is negatively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the upper or top quartile.Skewness of Box Plots. A box plot has positive skew if the median is nearer to the start of the plot and the first whisker is shorter than the last whisker. There is negative skew if the median is nearer to the end of the plot and the last whisker is shorter than the first whisker. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics of the symmetrical normal distribution with skewed distributions. When working with skewed distributions, it is essential to understand the key differences and similarities between positive and negative skewness. Both types of skewness exhibit asymmetrical shapes, but they differ in the direction of the skew.
Positive skew means a tail stretching right, while negative skew veers in the opposite direction. Kurtosis is all about peaks and tails. High kurtosis sharpens peaks and weighs down the tails, while low kurtosis spreads data, lightening the tails.
A negative value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the left side of the distribution, which extends towards more negative values. A positive value for skewness indicates that the tail is on the right side of the distribution, which extends towards more positive values. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score. Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of a distribution. A distribution is asymmetrical when its left and right side are not mirror images. A distribution can have right (or positive), left (or negative), or zero skewness.
A distribution is considered "Positively Skewed" when mean > median. It means the data constitute higher frequency of high valued scores. Negatively Skewed : For a distribution that is negatively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the upper or top quartile.Skewness of Box Plots. A box plot has positive skew if the median is nearer to the start of the plot and the first whisker is shorter than the last whisker. There is negative skew if the median is nearer to the end of the plot and the last whisker is shorter than the first whisker.
ptr 91 metal trigger housing
progressive sheet metal lavergne tn
positively skewed box and whisker
Service Roofing & Sheet Metal Company’s Martinsville location serves customers in southern and central Virginia and northern North Carolina in a 150-mile radius of Martinsville.
distribution of a box plot positive and negative skew|positive skewness boxplot